CBCT in the dental practice: Creating efficiencies and value
Dentists with busy referral practices are always looking for ways to increase efficiencies. With a well-trained team and the right technology, our practice has been able to reduce waste and deliver more value to our patients. Allow me to explain.
A smooth start
It all starts with a smart, flexible, and thoughtful team. From a procedural standpoint, having well-trained chairside team members dramatically streamlines the consultation process with patients. When team members are empowered to handle patient intake and gather key pieces of information for the dental visit, clinicians have everything they need to decide if advanced imaging is needed, which saves time and reduces waste—i.e., waste of skills or underutilizing team members’ capabilities. Using an efficient system, the patient flows smoothly through the consultation process: from intake to determination of imaging needs, to ordering and acquiring the appropriate imaging, and finally to the interpretation of results by the clinician. If imaging is needed, the team member can set up the intuitive cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) system, which is the CS 9600 (Carestream Dental) in our practice.
Reducing retakes
The process starts with the chairside team member and then moves on to the technologist. After acquiring a CBCT system, the team hones its skills and spends considerable time training and reviewing imaging studies so that potential mistakes during imaging can be identified and corrected before they become larger issues down the line.
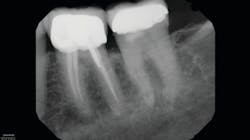
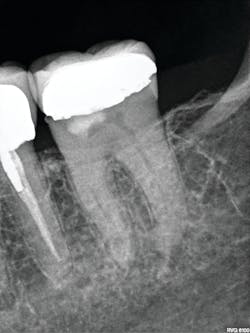
As a clinic based heavily on referrals, we get CBCT studies from other clinicians who invariably have used much larger FOVs than are needed. In endodontics, for example, dual-arch or larger studies expose patients to significantly more radiation and increased interpretation time—often at the expense of resolution for the areas of interest and imaging needs. This is likely done to reduce the chance of retakes due to poor alignment with systems that either don’t have scouting capability or only have it in a single plane.
With the CS 9600’s optional SmartAuto 3-D and 2-D scouts, structures of interest can be confirmed in the FOV, and the center of rotation is adjusted to optimize the ensuing study. In the past, and with extraoral systems that don’t have multiplanar scouting, retakes were not uncommon. Now, the ability to hit the target 100% of the time has allowed us to routinely use the smallest FOV (4 x 4 cm), which reduces the dose of radiation for patients.
Diagnosis and treatment planning
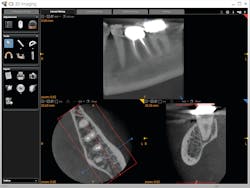
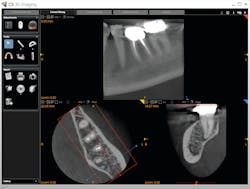
In more dense anatomic areas, more subtle radiographic findings that are not appreciated with projection radiography are visible in a passing glance with CBCT. Advanced imaging also helps with treatment planning and image-guided treatment (IGT). IGT, particularly in endodontics, allows a better estimation of the anatomic complexity and possible strategies for managing it. This also facilitates planned endodontic access to minimize the amount of sound tooth structure that is removed and maximize the remaining dentin.
Providing value to the patient
In a specialty practice, we often receive referrals of asymptomatic patients with existing chronic conditions, such as long-standing periapical findings on previously treated teeth and asymptomatic resorptions discovered with screening projection radiography. Advanced imaging allows us to do active surveillance with short-term follow-ups of six months to one year. In these cases, we can evaluate for interval change to help determine if the findings are correct, and then we can adjust treatment planning accordingly. The advanced features of our CBCT system allow us to provide added services to patients and referring doctors through referral-based imaging of the TMJ, teeth, sinus, and airways (with appropriate consultation with an ENT doctor), thus saving patients an extra trip to an imaging center.
The flexibility and advanced features of the CS 9600 coupled with a talented and flexible team, helps create efficiencies within the dental practice, from patient intake, to imaging, to treatment, and then to diagnosis.
About the Author

John A. Khademi, DDS, MS
John A. Khademi, DDS, MS, is a graduate of the University of California with a certificate in endodontics and the University of Iowa with a master’s in digital imaging. He is in private practice in Durango, Colorado, and lectures internationally on computer use in dental practice and conventional endodontic techniques. He is the lead author on Quintessence’s Advanced CBCT for Endodontics available on Amazon.