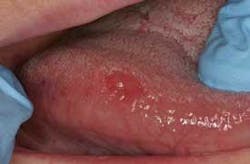
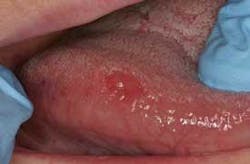
Two weeks ...the longest 14 days ever
For more on this topic, go to www.dentaleconomics.com and search using the following key words: oral cancer, lesions, early detection technologies, oral cancer screening, Dr. Kevin Huff.
It has been well established, discussed, and published that persistent suspicious variations in tissue appearance should be submitted for definitive histological diagnosis via excisional, incisional, or punch biopsies. These could be obvious erythroplakias, leukoplakias, or erythroleukoplakias. Most experts agree that a biopsy is indicated even in cases of apparent chronic inflammation that persist for two weeks after the source of injury — chemical or physical — has been identified and minimized. Those two weeks can be very stressful for patients in whom these early lesions have been identified.
From experience, I can attest to the fact that the “C” word, cancer, should be avoided at all costs. I believe that the emphasis has been incorrectly placed by manufacturers of early detection technologies on the point that these systems help to identify oral cancer. Most oral cancers probably are clinically obvious to the trained eye. Early oral cancer screening technologies are really designed to focus on lesions that are not clinically obvious and may hint at lesions that may become cancer in one to five years. Therefore, use of the expression, “we're using this light to find early oral cancer” probably is alarming and premature. Suggesting that a lesion may be — or may potentially be — cancer instills irrational fear for a majority of the population.
So, what should we say?
We, as dentists, have an ethical obligation to inform our patients if we find something significant during our examinations. Unfortunately, when we discover a pre–neoplasia or occult erythroplakia, leukoplakia, or spotted lesions, we are forced into situations where we typically have not been formally trained. Careful crafting of our words is the key to delivering unsettling news. It is critical to the psychological well–being of our patients to be informative and calm while not being overly alarming at the same time.
In the past, I was very forthright with my findings. It would not have been unusual for me to say matter–of–factly, “Mrs. Patient, I'm really concerned about this dark [white] spot that I found with this special light. We need to find out what it is, because it might be cancer.”
The reaction was nearly always the same — my patient leaving the office with watery eyes. Further, several of those patients left my practice because when they went to another dentist who did not have the early detection technology and got a second opinion, they were told there was “... nothing to worry about.” I failed on several levels. Most importantly, I may have caused those patients to lose confidence in the wonder of these new technologies that may have the potential to help save lives, and may have caused them to move to another dental practice that may not have been capable of detecting and managing those lesions, if indeed they were true neoplasia.
Experience has taught me to change the way I deliver the news of my findings. This script has proven to be helpful and well received:
“Hmm ... Mr. Patient ... this light helps us, along with the exam that I just did, to find things that may not be normal in your mouth. I see an area here that doesn't look quite normal. It's probably nothing to worry about, but I'd really like to take another look at it in two weeks. May I do that?”
By couching my observation like this, I have kindly informed my patient while still granting him or her control of the situation by asking permission for follow–up. My initial “Hmm ...” is very important, along with nonverbal facial expression in conveying my concern.
Depending on my patient's personality and initial reaction, I may or may not set the stage for follow–up at this time; however, caution is warranted because I really don't know at this point if the lesion is something that will require biopsy. Standard protocol dictates a 14–day reevaluation before that determination can be made. But if the patient appears to be very alarmed or frightened, I might suggest some form of immediate brush cytology for his or her peace of mind.
Early cancer detection technology is helping dentistry take a huge step toward improving cancer survival rates. However, the impact that our premature reactions and alarm can make to our patients' psychological health cannot be underestimated. Our patients need our empathy as well as our technology.
Kevin D. Huff, DDS, MAGD, is a practicing general dentist in rural Ohio, a private researcher, author, and dental educator. A clinical instructor at the Case School of Dental Medicine, he lectures nationally about oral cancer screening and biopsy techniques. Contact Dr. Huff at [email protected], or visit www.doctorhuff.net.